Daily Trend [11-24]
【1】Vision Transformers Need Registers
【URL】http://arxiv.org/abs/2309.16588
【Time】2023-09-28
一、研究领域
Self-surpervised ViT Networks,机器学习解释
二、研究动机
作者注意到许多 modern vision transformers 的注意力特征图中存在一些神秘的 artifacts(唯独除了 DINO 模型),特别是 DINO v2 也出现了类似的现象。于是这项工作中着手于更好地理解这种现象并开发检测这些 artifacts 的方法。
“In this paper, we identify and characterize artifacts in feature maps of both supervised and self-supervised ViT networks.”
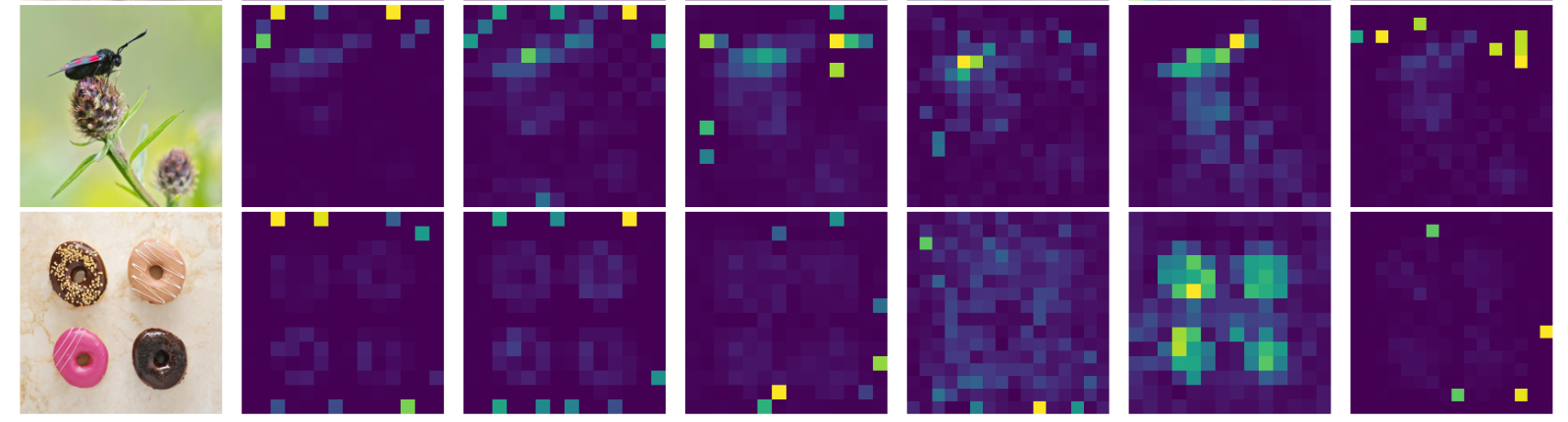
Illustration of artifacts observed in the attention maps of modern vision transformers.
三、方法与技术
提出假设:模型学习识别包含很少有用信息的 patch,并回收相应的 tokens 来聚合全局图像信息,同时丢弃空间信息。
We propose the following interpretation to these elements: the model learns to recognize patches containing little useful information, and recycle the corresponding tokens to aggregate global image information while discarding spatial information.
实验过程和观察结果:
(1)定义 artifacts (outliers) 是 “high-norm” tokens:作者观察到,“artifact” patches 和其他 patches 之间的一个重要区别是它们在模型输出中的 token embedding 的 norm,因此,将 norm 高于 150 的 tokens 视为 “high-norm” tokens,需要研究它们相对于 regular tokens 的性质。
结论1:Artifacts are high-norm outlier tokens.
(2)观察 outliers 出现的条件:在 DINO v2 的训练期间观察,发现这些 outliers 仅在三分之一的训练后出现,并且分析了六种不同尺寸的模型,发现只有三个最大的模型会表现出这种异常。
结论2:Outliers appear during the training of large models.
(3)观察 “high-norm” tokens 出现的位置:在 patch embedding layer 之后测量 “high-norm” tokens 与其 4 个邻居之间的余弦相似度,观察到高范数标记出现在与其邻居非常相似的 patch 上。这表明这些 patch 包含冗余信息,并且模型可以丢弃它们的信息而不损害图像表示的质量。
结论3:High-norm tokens appear where patch information is redundant.
(4)观察 “high-norm” tokens 包含多少局部信息:设计了两个任务,分别是 position prediction 和 pixel reconstruction,用于 probe the patch embeddings for different types of information。
- position prediction:训练一个线性模型来预测图像中每个 patch token 的位置,并测量其 accuracy。观察到 “high-norm” tokens 的准确度比其他 tokens 低得多,说明 “high-norm” tokens contain less information about their position in the image.
- pixel reconstruction:我们训练一个线性模型来根据 patch embeddings 预测图像的像素值,并测量其 accuracy。同样观察到 “high-norm” tokens 的准确度比其他 tokens 低得多,说明 high-norm tokens contain less information to reconstruct the image than the others.
结论4:High-norm tokens hold little local information.
(5)观察 “high-norm” tokens 包含多少全局信息:
- logistic classification:对于分类数据集中的每个图像,通过 DINO v2-g 网络处理它并提取 patch embeddings。然后从这些 patch embeddings 中,随机选择一个 token,无论是 high-norm 还是 regular 的。然后将该 token 视为 image representation。然后,训练一个 logistic regression classifier 以根据该 image representation 来预测图像类别,并测量其 accuracy。观察到 “high-norm” tokens 的准确度比其他 tokens 高得多,说明 “high-norm” tokens contain more global information than other patch tokens.
结论5:Artifacts hold global information.
根据实验结果修正假设:经过充分训练的大型模型学习识别冗余标记,并将它们用作存储、处理和检索全局信息的位置。
Having made these observations, we make the following hypothesis: large, sufficiently trained models learn to recognize redundant tokens, and to use them as places to store, process and retrieve global information.
根据修正的假设提出问题:这种行为会导致模型丢弃局部补丁信息,从而可能导致密集预测任务的性能下降。
Furthermore, we posit that while this behavior is not bad in itself, the fact that it happens inside the patch tokens is undesirable. Indeed, it leads the model to discard local patch information (Tab. 5b), possibly incurring decreased performance on dense prediction tasks.
提出解决方案:明确地将新的 token 添加到序列中,模型可以学习将其用作寄存器。特别地,这些添加到序列中的 token 不为模型添加任何信息,并且它们的输出值不用于任何目的,也不需要对它们做任何监督。这些 “无用” 的 token 将代替本该出现的 High-norm tokens 扮演 “寄存器” 的角色。方案非常简单,如下图的 pipeline 所示:
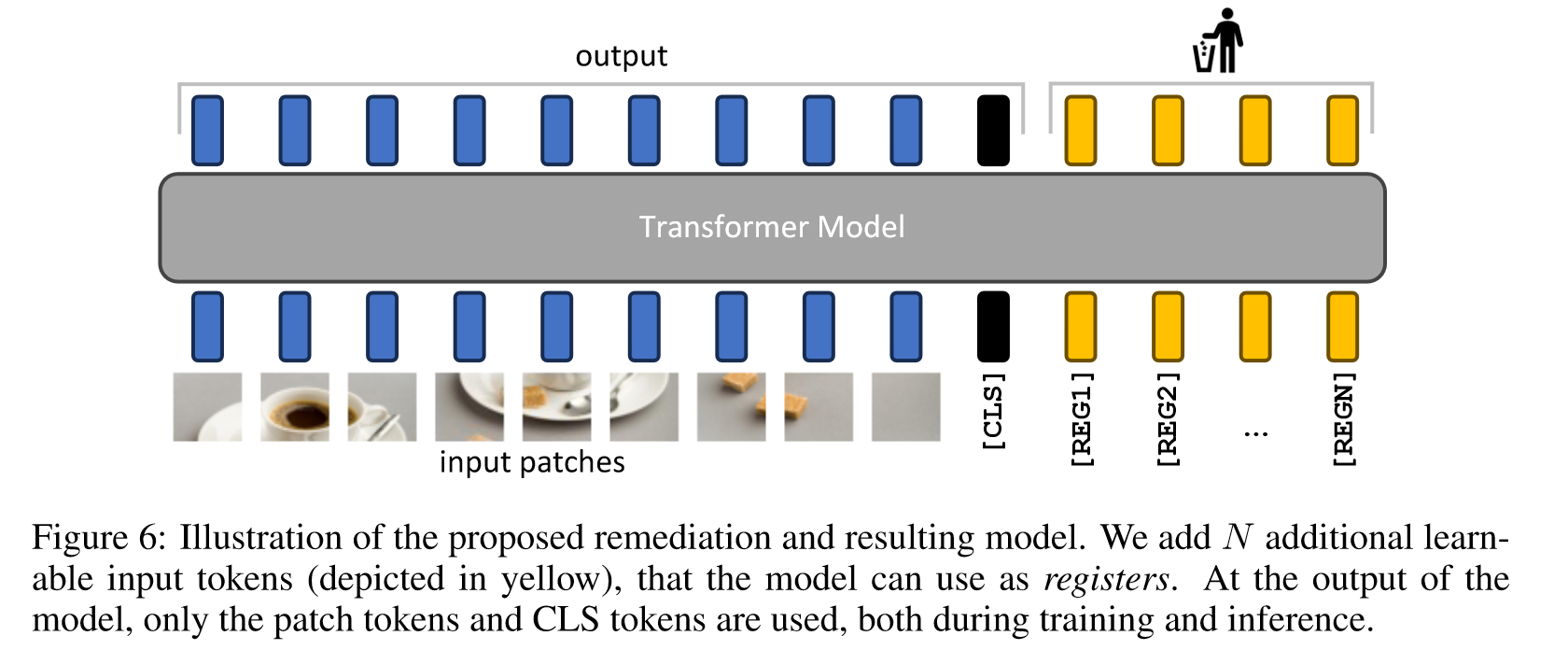
四、总结
无论是从 setting, experiments, 还是 conclusion 来说,这都是特别特别有意思的一项工作。最终论证了为模型显示添加一些看似毫无用处的 token 可以大大提升它的性能,也解释了较大的视觉模型工作过程中会自发地形成一些类似于 “寄存器” 的东西来帮助其记忆全局信息。
五、推荐相关阅读
Memory transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.11527, 2020.