Daily Trend [12-12]
【1】Sequential Modeling Enables Scalable Learning for Large Vision Models
【URL】http://arxiv.org/abs/2312.00785
【Time】2023-12-01
一、研究领域
Large Vison Model
二、研究动机
提出一种纯视觉的顺序建模方法,在不使用任何语言数据的情况下学习大型视觉模型(LVM)。理由是视觉能力不依赖于语言(这一点也体现于动物世界中):
Large language models (LLMs) such as GPT [11] and LLaMA [80] have taken the world by storm. What would it take to build a Large Vision Model (LVM)? From the animal world, we know that visual competences are not dependent on language. In particular, many experiments have shown that the visual world of non-human primates is remarkably similar to that of humans. So while the space of vision-language models such as LLaVA [54] is interesting and worthwhile to pursue, in this paper we seek an answer to a different question – how far can we go from pixels alone?
三、方法与技术
数据集:构建一个前所未有的统一大视觉数据集UVDv1
(1)单张图片:本身就是一个句子 {image, EOS},主要来自于数据集 LAION 5B。
(2)图片序列: 包括三种序列。第一种来自于视频数据,以按一定步长采样的每16帧作为一个序列;第二种来自于3D数据,以按一定相机位姿采样的每24个视角作为一个序列;第三种来自于imagenet图片数据,以按类别划分的每16张图片作为一个序列。
(3)带标注的图片:统一将所有标注转为图像形式(例如:用带颜色的框来注释目标检测;用mmpose来绘制人体姿态;深度估计、法线和边缘检测、风格转移、去噪、修复等),然后将图片与其标注作为图像对,将具有同类型标注的每8个图像对连接成16个图片的句子。
(4)带标注的图片序列:首先同理将标注转为图像形式,然后将序列里的图片单独或者分组与相应的标注图片配对,前后连接形成句子。

Figure 1. Visual sentences allow us to format diverse vision data into the unified structure of image sequences.
训练过程:两阶段方法(Image Tokenization+Sequence Modeling)
(阶段1)训练一个 large visual tokenizer:具体而言,使用现成的 VQGAN tokenizer,在 LAION 5B 数据集上训练,学习将每张图片映射到 256 个离散 tokens,码表大小是 8192。
(阶段2)为 visual sentences 训练一个 autoregressive transformer model:将得到的 visual tokens 连接成一维序列,每 16 张图像的 tokens 构成一个 visual sentences,前后添加标记符号 [BOS] 和 [EOS],使用现成的 LLaMA 结构,在 UVDv1 数据集上训练,学习自回归的 visual tokens 预测。
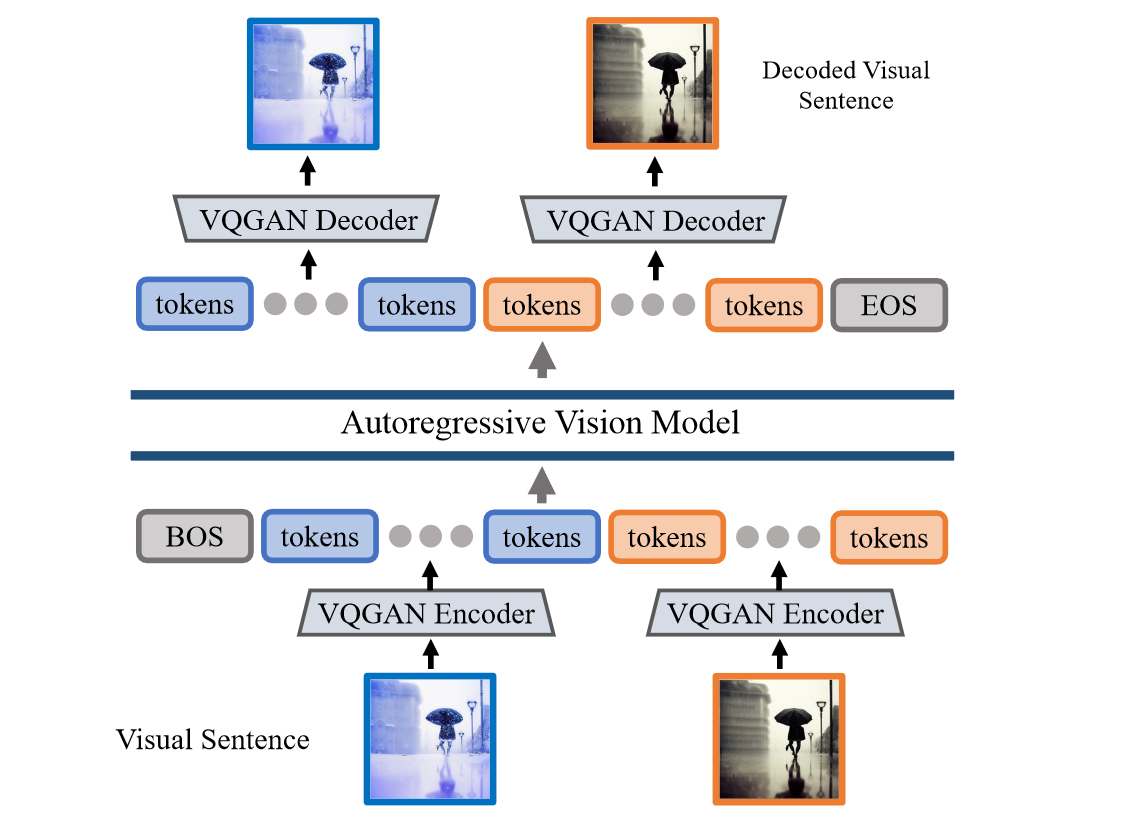
Figure 2. Architecture of LVM. We first convert individual images from a visual sentence into discrete tokens using a VQGAN encoder. The resulting tokens from all images are then concatenated into a 1D sequence, and fed into an autoregressive Transformer model to predict the next token in the sequence. The predicted visual tokens are decoded into images using the VQGAN decoder.
推理阶段:visual prompting
和 LLM 是一样的道理,只是把 text prompt 换成了纯 visual prompt。
实验
作者首先通过调整数据集多样性和训练程度说明了 LVM 是 scalable 的,然后通过后续视频帧生成任务展示了顺序推理的能力,还用一些 IQ 测试和图推题测试了 LVM 在未见任务上的泛化能力。作者认为工作的 limitation 主要是计算资源。
LVM not only benefits from larger data, but also improves with more diversity in the dataset, which includes both annotated and unsupervised image and video data.
四、总结
最朴素的方式大力出奇迹。虽然 LVM 也许真的是 AGI 的小火花,但是考虑到数据的多样性非常非常高,模型的所谓泛化能力是否真的可信还存疑。
(该文章发布的知乎评论区下还可以吃到原作和谷歌的大瓜)